Hyperpigmentation Face/ Facial melanoses
Facial melanoses (FM) are a common presentation in Indian patients, causing cosmetic disfigurement with considerable psychological impact. Melasma is one of the many different causes of Hyper-pigmentation of Face (Facial Melanoses)
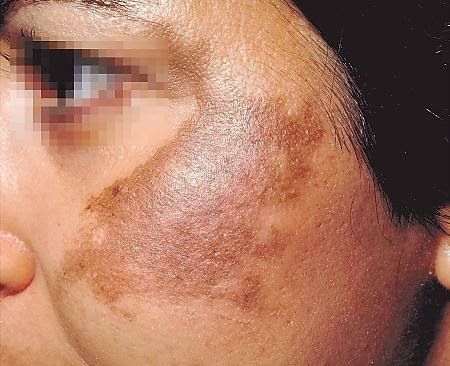
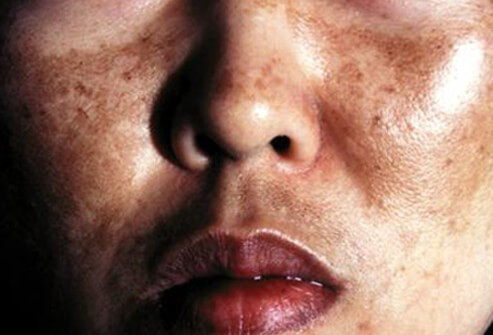
MELASMA (CHLOASMA)
Who gets melasma?
Melasma is commoner in darker skin types being most common in people with light brown skins, especially in people of East and South East Asian and Hispanic origin who live in areas with intense solar ultraviolet radiation (UVR).
It is commoner in women than in men (9:1) and is rare before puberty, occurring most commonly in women of reproductive age.
What causes Melasma?
- The exact etiology of melasma is not known but several factors have been implicated.
- Ultra Violet Rays (UVA and UVB) and visible light cause peroxidation of lipids in cellular membranes, leading to generation of free radicals, which stimulate melanogenesis.
- Elevated levels of estrogens and progesterone (as occurring in pregnancy) are important.
- Birth control pills may also cause melasma.
- Melasma is several times commoner in patients with thyroid disease
- People with a family history of melasma are more likely to develop melasma.
Diagnosis of Melasma
Melasma has a characteristic appearance on the face, most patients can be diagnosed simply by a skin examination. Occasionally a skin biopsy is necessary to differentiate melasma from other conditions.
Treatment of Melasma
Melasma causes cosmetic disfigurement with significant emotional impact.
Its treatment includes
- Removal of provoking factors
- Vigorous photoprotection and
- Active pigment reduction either with Topical agents or physical procedures like Chemical peels, Lasers and Dermabrasion.
There is no universally effective specific therapy — existing agents have varying degrees of efficacy and relapses are frequent.
Photoprotection
Photoprotection is essential, because photo darkening can occur with just a couple of hours of sun exposure
Sunscreens
Opaque sunscreens containing zinc oxide, 10% (and SPF of 30) have dual benefit of camouflaging FM and preventing photo-induced darkening.
Avoidance of provoking factors
Avoiding triggers is necessary in melasma
Lightening agents
Topical agents like Hydroquinone, Azelaic acid, Kojic Acid, Retinoids, Glycolic acid, Niacinamide, Ascorbic Acidneed to be used for several months before effect becomes apparent.
Combination treatment
Topical agents act on different stages of melanogenesis, therefore when combined give better therapeutic
results.
Chemical peels
Chemical peels can used to treat Melanosis either as stand alone treatment or combined with other modalities.
Lasers for melasma
Q switched Nd YAG laser may help in melasma